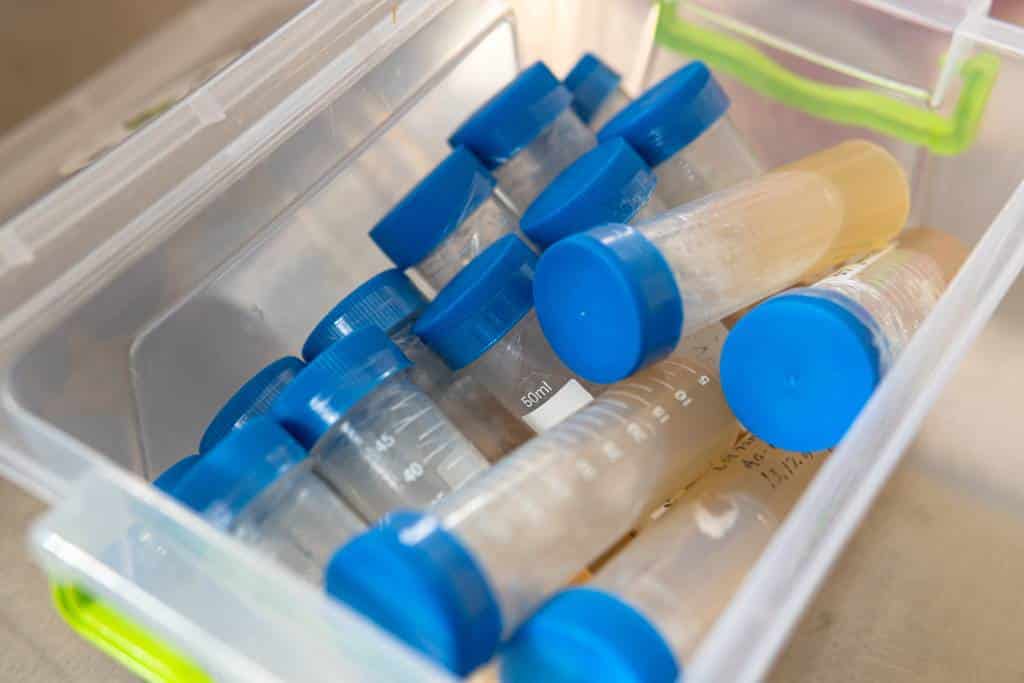
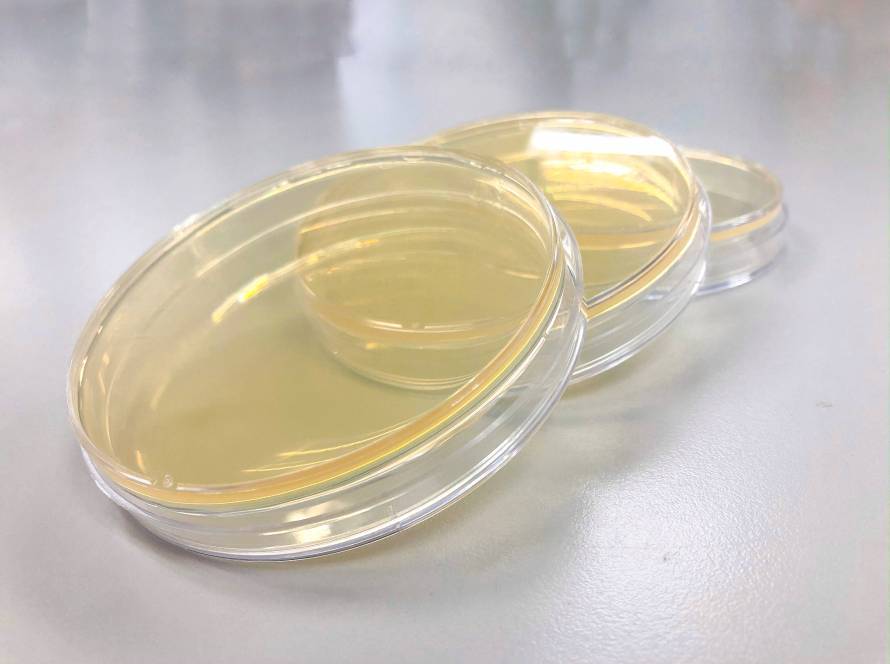
If you’re starting out in the world of mycology, it’s important to understand the difference between agar plates and agar slants. While both are used to grow and maintain cultures of fungi and other microorganisms, they serve different purposes and have their own unique advantages and disadvantages.
Agar plates are flat, circular dishes filled with agar and other nutrients that have been sterilized to eliminate any potential contaminants. These plates are used to cultivate fungi and other microorganisms for observation, identification, and experimentation. They’re typically used for short-term storage and are ideal for observing the growth and morphology of a culture over time. The primary advantage of agar plates is their large surface area, which allows for the growth of a large number of colonies in a relatively small space. This makes it easy to observe and identify different types of fungi, as well as to test different experimental conditions.
On the other hand, agar slants are long, thin tubes filled with agar and other nutrients that have been sterilized to eliminate any potential contaminants. These tubes are used to maintain cultures of fungi and other microorganisms for long-term storage. The primary advantage of agar slants is their compact size, which allows for easy storage in a refrigerator or other cold storage unit. This makes them ideal for maintaining cultures over extended periods of time without the need for regular subculturing.
So, while agar plates are ideal for observing and experimenting with different cultures of fungi and other microorganisms, agar slants are better suited for long-term storage of those cultures. Both are essential tools for anyone working in the field of mycology and provide important insights into the complex world of fungi and other microorganisms.